Burnout.
Give me something I love, and I’ll find a way to make myself hate it.
I don’t mean people or even objects; I mean things I do. Let me get a whiff of being good at something, and I’ll want to be the best – or at least the best I can be.
The cycle.
The harder I work at getting better, the better I get, then the harder I work, and then… do I get even better? Actually, after a few cycles, that’s when I stop entirely, because I’ve burned myself out.
Then the separate cycle of despair over not being as good as I could be starts, and it takes me a while to work up enough momentum to fling myself out of that orbit into being obsessed with being good at something again.
There’s not a lot of time left for enjoying yourself in this pattern, is there?
I loved art before, when I was younger and the purpose of art was to make art, to be part of it and not just to see it. After I dropped out of art school at 20 to have an unsuccessful stab at happy housewifery, I felt as though I’d betrayed my real self, and that was the start of the trouble with art.
I couldn’t blame anyone but myself, because I’d stopped myself from getting better. I did try to push through on my own, but nothing connected until I enrolled in art school again, at 31.
This time, I was going to squeeze eleven years’ worth of practice into two years of education, and I was going to come out of the other side with my old life back.
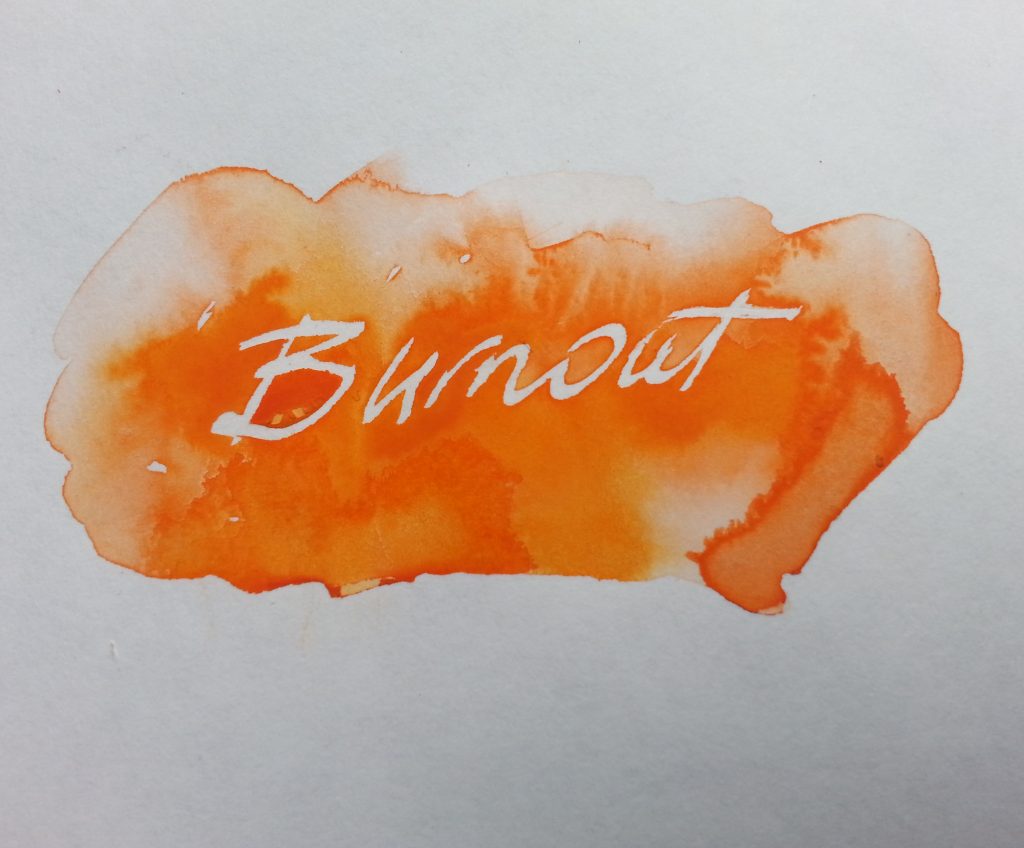

Reality.
Of course, that couldn’t happen. Private views, residencies, commissions – these are easy when you’re fresh out of college and don’t have to fit in the school run.
I tried to take on as much as I could, because the sky would fall down on my head if I didn’t hit the ground running. After all, getting a job with the word ‘art’ in the title would prove that I was worth something, right?
Suddenly, the happiness of finally getting that BA in Fine Art (with a lovely 1st class to add to the CV) bled into dread of not being able to get a job, and of having to face the dreaded JobCentre and the supercilious agents of employment scorn therein. Then, the happiness of finding a job! Of being asked to start a band! Of getting onto an MA course! Of moving to London!
Overwhelm strikes…
Such a lot of happiness all at once… of course, I had to keep my job, practise with the band in Kent, study for the MA and raise my son as a single parent and be the best I could be at all of them at the same time. But, the thing was, I missed making.
The MA was challenging and interesting, but the studios at Goldsmiths looked so much more appealing than the library. I started to wonder if I was the only one who thought that the theory wasn’t half as important as the art itself. I thought I was.
It was starting to look like a very expensive mistake, as if it was all for the sake of some more letters after my name to prove I was worth something.
The job was good, but was physically very tiring sometimes. It would only be there for another few months, and then I’d have to find another one – panic. The singing was incredible fun and the band had my name on it, which was all a dream come true, but it took me an hour and a half to drive to rehearsals each Saturday and then an hour and a half back home, and the same for gigs.
It took four months for me to crack, but I did crack. I got so physically run down that I became depressed. I had the flu for about a month, lost my voice and barely recovered in time for our first gig.
Change
A few months later (this is the short version), I had the answer handed to me by my deus ex machina in the form of my future husband, who picked me up and dropped me in Lancashire and made me get on with life away from the things I loved that weren’t loving me back enough.
Three years on, the sky didn’t fall down because I’ve only had a few exhibitions. My son loves me as much now as he did when I didn’t have two degrees. I have a job with ‘art’ in the title and I can still find something to complain about. No-one who loves me cares that I’ve never been an artist in residence anywhere and I stopped caring as well.
What am I doing now? Two websites for two separate businesses, a half-started novel, a part-time job, and a full-time family. Sounds like I haven’t learned, right? Only this time, everything else has to come after what’s best for me and my family. If you’re panicking about what comes next in your art career, don’t. Seriously, don’t.
I’m happier now that I’ve stopped panicking and started living.
You can make something happen by simply making your own work for your own gratification and making your own opportunities. Panicking won’t help. It certainly won’t help you to enjoy your life.
Make your (art)work fit your life, and you’ll realise there’s nothing to prove – you’re already worth something.
Register your interest in the Art & Money – Personal Finance + Professional Practice course.